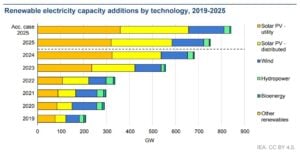
The world’s renewable energy sector has entered a new phase of record growth. According to the International Energy Agency’s Renewables 2025 report, global renewable power capacity grew by more than 510 gigawatts (GW) in 2024 — the fastest increase ever recorded. Another 520 GW is expected to be added in 2025, pushing renewables to account for over 90% of all new global power capacity.
Solar and wind dominate this growth. By 2025, solar will account for nearly three-quarters of new installations. This growth comes from cheaper technology, improved grid integration, and supportive policies. Wind power is also recovering after a slowdown in 2022–2023, supported by new offshore projects in Europe, China, and the United States.
The IEA says the world’s total renewable capacity will reach nearly 5,800 GW by 2025, up from around 4,200 GW in 2023. That means renewables now generate about 30% of global electricity and are on track to reach 42–45% by 2030.
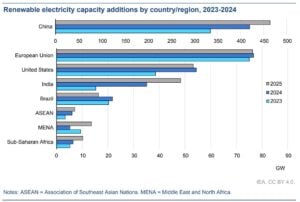
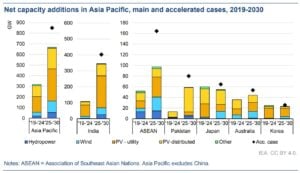
Four regions — China, Europe, the United States, and India — are responsible for almost 90% of this global expansion. Each is moving at a different pace, but together they are transforming how the world produces and consumes energy.
Europe: Accelerating the Energy Transition
Europe continues to lead in energy policy and innovation. In 2024, the European Union added more than 70 GW of new renewable capacity, driven mainly by solar. This is a record year. It shows the bloc’s goal to cut reliance on imported fossil fuels. They aim to meet their Green Deal target of a 55% emissions reduction by 2030.
Solar capacity across the EU doubled between 2020 and 2024, reaching over 300 GW, while wind capacity passed 220 GW. The IEA predicts that Europe will add 450 GW of renewables from 2025 to 2030. This will raise the total capacity to almost 870 GW by the end of the decade.
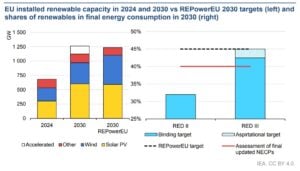
Much of this growth is tied to the REPowerEU plan, which aims to speed up permitting and expand rooftop solar. Offshore wind is gaining popularity. Countries like Germany, Denmark, and the Netherlands are investing in North Sea projects.
Despite progress, Europe faces challenges. Delays in grid expansion and limited local manufacturing capacity for wind turbines have created supply bottlenecks. Even so, strong policy support and high carbon prices still make renewables the best choice for power generation.
United States: Policy Support and Private Investment Drive Expansion
The United States is entering a period of major renewable growth, supported by the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and record private investment. The IEA expects the U.S. to add around 400 GW of new renewable capacity by 2030, effectively doubling its current base.
In 2024, U.S. solar installations rose by nearly 40%, reaching 45 GW for the year. Solar now accounts for the largest share of new capacity additions. Wind power also recovered, with onshore and offshore projects expanding in Texas, California, and along the East Coast.
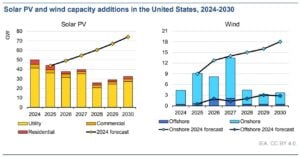
Renewables currently generate about 26% of U.S. electricity, up from 22% in 2022. The IEA projects this share will climb to over 40% by 2030, driven by federal tax incentives and falling technology costs.
Battery storage is another fast-growing sector. Storage capacity doubled between 2023 and 2024, helping stabilize variable solar and wind output. The IRA’s clean energy credits could draw over $400 billion in investments by 2032. This boost will help generate energy and support U.S. manufacturing of solar panels and turbines.
Challenges remain. The U.S. needs to modernize its grid and streamline permitting for transmission lines to connect renewable projects to demand centers. But the direction is clear — renewables are becoming the backbone of America’s energy system.
China: The Global Powerhouse of Renewables
China remains the undisputed leader in renewable energy growth. The IEA projects that China will account for about 60% of all new renewable capacity added worldwide by 2030.
In 2024 alone, China installed more than 260 GW of new renewables — more than the rest of the world combined. Solar made up the majority of this, with over 190 GW of solar capacity added during the year.
Wind power grew by 60 GW. China kept building big onshore and offshore projects in Inner Mongolia, coastal areas, and deserts.
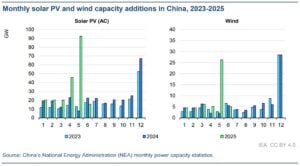
China now has an estimated 1,400 GW of total renewable capacity, representing about half of the global total. Renewables already supply more than 35% of China’s electricity, up from 27% in 2020.
Government policy is the key driver. China aims to reach 1,200 GW of combined solar and wind capacity by 2030, a target it is likely to achieve five years early. The country’s large manufacturing base keeps equipment prices low globally. This helps other regions grow their clean energy fleets.
Still, integration challenges persist. Some provinces face grid congestion and curtailment — when renewable power can’t be used due to transmission limits. The IEA recommends that China continue to invest in grid upgrades and flexible storage systems to handle its rapid growth.
India: The Fastest-Growing Emerging Market for Renewables
India is now the fastest-growing renewable energy market among developing economies. The IEA expects India’s renewable capacity to nearly double between 2023 and 2030, expanding from around 190 GW to 360–380 GW.
Solar energy is leading the charge. In 2024, India added more than 17 GW of solar capacity, supported by large auctions and declining costs. Wind capacity also grew modestly, and new hybrid projects combining solar and wind are improving reliability.
The government’s goal is ambitious: 500 GW of non-fossil capacity by 2030, which would cover about 50% of total power demand. India is also expanding its domestic solar manufacturing base to reduce dependence on imports.
Hydropower and bioenergy continue to play supporting roles, particularly in rural electrification. The IEA reports that renewable energy in India cuts over 250 million tonnes of CO₂ emissions each year. This makes India a major player in global emission reductions, second only to China.
However, financing and grid infrastructure remain key hurdles. The report notes that India needs annual clean energy investments of about $60–70 billion through 2030 to meet its targets.
The chart below compares renewable energy capacity in 2024 vs. 2030 projections for the four key regions, based on the IEA Renewables 2025 report.
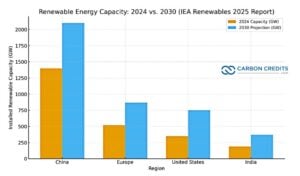


It clearly shows China’s dominant position, followed by steady growth in Europe and the U.S., and rapid expansion in India’s renewable capacity by the end of the decade.
The Decade of Clean Power: A Turning Point for Global Energy
The combined momentum of China, Europe, the United States, and India is reshaping global energy markets. Together, these four regions will account for almost 90% of all renewable capacity growth by 2030.
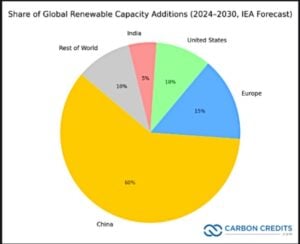
The pie chart shows each region’s share of total global renewable capacity additions from 2024 to 2030, based on the IEA forecast. It also shows how dominant China remains in driving renewable expansion, while Europe, the U.S., and India together account for about one-third of the world’s clean-energy growth.


Global renewable electricity capacity is expected to surpass 6,200 GW in 2025 and reach 8,300 GW by 2030 — roughly triple the total in 2015. Solar will remain the dominant source, followed by wind and hydropower.
Yet challenges persist. The IEA warns that grid constraints, permitting delays, and uneven financing could slow progress in developing economies. To stay on track for the net-zero pathway, annual renewable additions must rise to around 800 GW per year by 2030.
Still, the direction is clear. The world is entering a decade where clean power becomes the main driver of growth, investment, and energy security. The actions of these four key players will determine how fast the transition happens and how close we come to a truly sustainable global energy system.






